🐥 Session 2 (“Intermediate”)

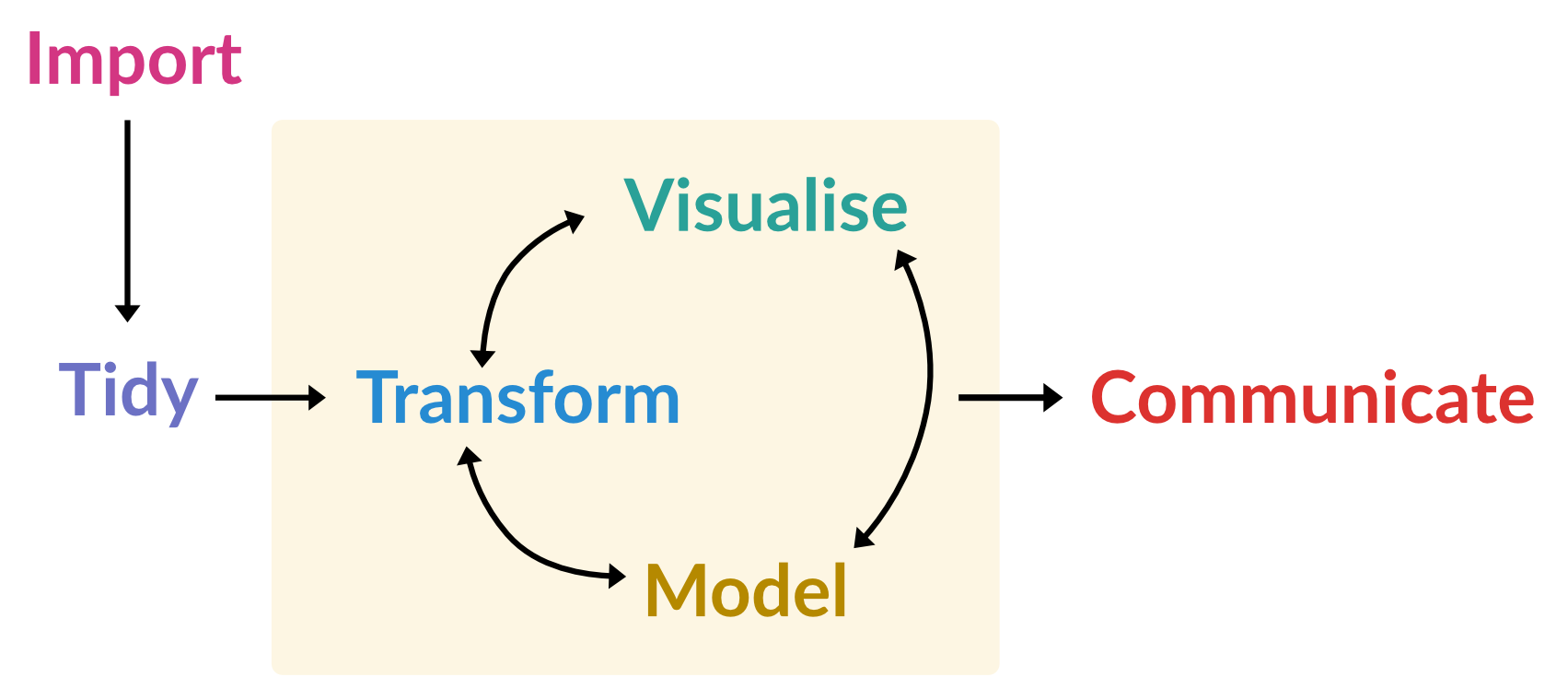
This session will begin by introducing key concepts in R programming, including functions, iteration, and control flow. You’ll learn how to create your own functions to automate repetitive tasks and streamline your workflows. We’ll also explore iteration techniques, discussing R-specific approaches to handling repeated operations efficiently.
In the second half of the session, we’ll focus on essential data manipulation tasks in R. This will include an introduction to the tidyverse, a powerful collection of packages designed to simplify and enhance data analysis. Through hands-on examples, we’ll cover core steps for working with data, including:
- Selecting columns or rows
- Sorting datasets
- Creating or modifying columns
- Combining datasets
- Reshaping datasets
- Grouping and summarising data
Timetable
Practical solutions
This section contains solutions to the reshaping practical at the end of the ‘Data manipulation’ lecture.
- Reshape the
fish_encountersdataset to ‘wide’ format, such that each column represents a different monitoring station.
- After reshaping, is this dataset ‘tidy’? Why?
- Reshape the world_bank_pop dataset to ‘long’ format, such that it contains three columns:
country,indicator,year, andvalue.
head(world_bank_pop)# A tibble: 6 × 20
country indicator `2000` `2001` `2002` `2003` `2004` `2005` `2006`
<chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 ABW SP.URB.TOTL 4.16e4 4.20e+4 4.22e+4 4.23e+4 4.23e+4 4.24e+4 4.26e+4
2 ABW SP.URB.GROW 1.66e0 9.56e-1 4.01e-1 1.97e-1 9.46e-2 1.94e-1 3.67e-1
3 ABW SP.POP.TOTL 8.91e4 9.07e+4 9.18e+4 9.27e+4 9.35e+4 9.45e+4 9.56e+4
4 ABW SP.POP.GROW 2.54e0 1.77e+0 1.19e+0 9.97e-1 9.01e-1 1.00e+0 1.18e+0
5 AFE SP.URB.TOTL 1.16e8 1.20e+8 1.24e+8 1.29e+8 1.34e+8 1.39e+8 1.44e+8
6 AFE SP.URB.GROW 3.60e0 3.66e+0 3.72e+0 3.71e+0 3.74e+0 3.81e+0 3.81e+0
# ℹ 11 more variables: `2007` <dbl>, `2008` <dbl>, `2009` <dbl>, `2010` <dbl>,
# `2011` <dbl>, `2012` <dbl>, `2013` <dbl>, `2014` <dbl>, `2015` <dbl>,
# `2016` <dbl>, `2017` <dbl>longer <- world_bank_pop |>
pivot_longer(
`2000`:`2017`,
names_to = "year",
values_to = "value",
names_transform = parse_number
)- Reshape the
table2dataset such that there are separate columns forcasesandpopulation.
head(table2)# A tibble: 6 × 4
country year type count
<chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 Afghanistan 1999 cases 745
2 Afghanistan 1999 population 19987071
3 Afghanistan 2000 cases 2666
4 Afghanistan 2000 population 20595360
5 Brazil 1999 cases 37737
6 Brazil 1999 population 172006362table2 |>
pivot_wider(names_from = type,
values_from = count)# A tibble: 6 × 4
country year cases population
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 Afghanistan 1999 745 19987071
2 Afghanistan 2000 2666 20595360
3 Brazil 1999 37737 172006362
4 Brazil 2000 80488 174504898
5 China 1999 212258 1272915272
6 China 2000 213766 1280428583